A gap analysis is a formal study that identifies the gap between a business’s current situation and its future needs in terms of performance, processes, sales, systems, and organizations, or it may be Business, Technology, Products/Services against the future situation or needs. The study could be restricted for the department’s particular function, product, or location, or it could be an enterprise wide analysis. Gap Analysis actually defines the benchmarking of future portfolios, systems, or processes.
Although the scope of this blog is restricted to IT Business Analysis, we need to discuss this topic in detail so that the Business Analyst can get the detailed perspective of the gap analysis done using various scenarios, such as:
- Business Process / Industry standards Analysis
- Products & Services Analysis
- IT Systems Analysis
- Compliances Analysis
- Technology Analysis
- Performances Analysis
Business Process / Industry Standards Analysis:
If an organization decided to improve their overall processes, they could do so by implementing ISO ® or just adhering to Verisign® security requirements related to a secured online payment process for their website for receiving online payment. In both of these cases, there could be significant impact on the functioning of respective department(s) where changes are expected. Thus, the Gap Analysis is needed to identify and define future requirements for the solution.
Product & Services Analysis:
Based on the company’s projection, there could be requirements or plans to expand an existing portfolio by adding new products or discontinuing existing product(s). These are very high-level Gap analyses that are done keeping the future growth of the company and future need of the consumer in mind. In this case, the company’s profit and shareholder interest are taken into consideration. For example, considering the demand and future need of healthy food, Pepsi decided to enter into the healthy food market and planned to acquire the Tropicana ® and Quaker ® brand to expand Pepsi’s portfolio. Market potential, usage gap, and competitive gaps are other factors to be considered while undertaking the Gap Analysis.
Compliances Analysis:
Recently, there have been new compliances introduced by financial regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), as well as other such bodies in their respective countries. These compliances deal with (possible) financial frauds or are intended to ease out the business process. A recent change introduced by the SEC was “Locate the Stock” in the "Short-Selling" process in 2005. Similarly, in 2010, the SEBI, through Mutual Funds Amendment regulations, introduced new timeframes in conducting Mutual Fund business.
Technology Analysis:
Enterprise-wide analysis will facilitate defining the Gap between the outdated technology that exists and current and/or future needs of the new technology/machines that will improve the production/services of a company. For example, offset printing machines versus digital printing machines with the latest features offered by Hewlett Packard.
In Information Technology, the term GAP analysis is defined as the detailed study of the gap between future systems or the requirement or process (which is known as “TO-BE” which means the way it should be or is “to be”) and the current system or process (which is known as “AS-IS” i.e. meaning the way it is or “as it is”).
Basis of GAP Analysis:
Here is the simple equation for us to start.
GAP Analysis = TO-BE – AS-IS
A Gap analysis is accomplished using various criteria such as functionalities, technology, compliances, legal issues, industry standards, performance, and look and feel.
Functionalities: Due to changes in processes, products, or services, the organizations need to build new systems or modify the existing ones. The changes could be minor or could lead to building entire new systems.
Technologies: The reality is that today’s latest technology is dated tomorrow. Nothing changes faster than technology, thus professionals tend to migrate toward new technology to keep them up-to-date for their career race. Organizations find it difficult to hire technical support professionals to operate and maintain systems built using outdated languages (such as COBOL, Pearl, etc.).
In addition, the old technology brings new security threats, as these dangers get more complex by each day, as well as other technical limitations needed to accommodate new changes in the system.
Legal/Compliances: With business processes getting more intricate, the threat to business owners and investors is getting equally complex. In order to avoid extreme damages, such as bankruptcy (as happened in infamous Enron company where many investors, especially retired people, lost money in the stocks), the government introduced new compliances, Sarbane-Oxlay for bring transparency to corporate accounting systems. With this new compliance, every company in United States has to change their accounting system to accommodate this law.
Industry Standards: Industry standards keep enhancing, evolving with new trends and innovations. For example, most of the industry would now prefer to convert their products to something more environmentally friendly to appeal to their customers.
Performance: With increased business and complex technology, there will be a greater load on the system, thus, these systems need to cope with complexity and increased load.
For example, booking airline tickets 20 years ago was far less complex than it is today. The number of travellers and complexity of the system has grown tremendously.
Look and Feel: Every company has to update its website based on new standards and trends in the market. This helps to boost the business and buying experience of the consumer. Some of the e-commerce websites dealing in garments were actually helping consumers get the fitting room experience by allowing them to enter the data and choosing a particular garment. Then, the application would show the buyer how he/she would look in that outfit.
Other: Any other reasons that not listed above.
Let us see what the GAP analysis will look like using these criteria:
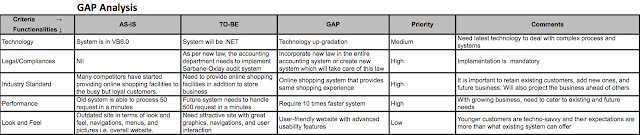
This is a high-level document. Readers are strongly recommended to study it in detail for a better result as the GAP analysis (criteria, process, and result) may change based on domain and company's internal policies/culture.
Disclaimer: ISO®, Tropicana®, Hewlett-Packard®, VeriSign® their trademarks and respective product names are used here only for reference to explain the point in the blog.
Although the scope of this blog is restricted to IT Business Analysis, we need to discuss this topic in detail so that the Business Analyst can get the detailed perspective of the gap analysis done using various scenarios, such as:
- Business Process / Industry standards Analysis
- Products & Services Analysis
- IT Systems Analysis
- Compliances Analysis
- Technology Analysis
- Performances Analysis
Business Process / Industry Standards Analysis:
If an organization decided to improve their overall processes, they could do so by implementing ISO ® or just adhering to Verisign® security requirements related to a secured online payment process for their website for receiving online payment. In both of these cases, there could be significant impact on the functioning of respective department(s) where changes are expected. Thus, the Gap Analysis is needed to identify and define future requirements for the solution.
Product & Services Analysis:
Based on the company’s projection, there could be requirements or plans to expand an existing portfolio by adding new products or discontinuing existing product(s). These are very high-level Gap analyses that are done keeping the future growth of the company and future need of the consumer in mind. In this case, the company’s profit and shareholder interest are taken into consideration. For example, considering the demand and future need of healthy food, Pepsi decided to enter into the healthy food market and planned to acquire the Tropicana ® and Quaker ® brand to expand Pepsi’s portfolio. Market potential, usage gap, and competitive gaps are other factors to be considered while undertaking the Gap Analysis.
Compliances Analysis:
Recently, there have been new compliances introduced by financial regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), as well as other such bodies in their respective countries. These compliances deal with (possible) financial frauds or are intended to ease out the business process. A recent change introduced by the SEC was “Locate the Stock” in the "Short-Selling" process in 2005. Similarly, in 2010, the SEBI, through Mutual Funds Amendment regulations, introduced new timeframes in conducting Mutual Fund business.
Technology Analysis:
Enterprise-wide analysis will facilitate defining the Gap between the outdated technology that exists and current and/or future needs of the new technology/machines that will improve the production/services of a company. For example, offset printing machines versus digital printing machines with the latest features offered by Hewlett Packard.
In Information Technology, the term GAP analysis is defined as the detailed study of the gap between future systems or the requirement or process (which is known as “TO-BE” which means the way it should be or is “to be”) and the current system or process (which is known as “AS-IS” i.e. meaning the way it is or “as it is”).
Basis of GAP Analysis:
Here is the simple equation for us to start.
GAP Analysis = TO-BE – AS-IS
A Gap analysis is accomplished using various criteria such as functionalities, technology, compliances, legal issues, industry standards, performance, and look and feel.
Functionalities: Due to changes in processes, products, or services, the organizations need to build new systems or modify the existing ones. The changes could be minor or could lead to building entire new systems.
Technologies: The reality is that today’s latest technology is dated tomorrow. Nothing changes faster than technology, thus professionals tend to migrate toward new technology to keep them up-to-date for their career race. Organizations find it difficult to hire technical support professionals to operate and maintain systems built using outdated languages (such as COBOL, Pearl, etc.).
In addition, the old technology brings new security threats, as these dangers get more complex by each day, as well as other technical limitations needed to accommodate new changes in the system.
Legal/Compliances: With business processes getting more intricate, the threat to business owners and investors is getting equally complex. In order to avoid extreme damages, such as bankruptcy (as happened in infamous Enron company where many investors, especially retired people, lost money in the stocks), the government introduced new compliances, Sarbane-Oxlay for bring transparency to corporate accounting systems. With this new compliance, every company in United States has to change their accounting system to accommodate this law.
Industry Standards: Industry standards keep enhancing, evolving with new trends and innovations. For example, most of the industry would now prefer to convert their products to something more environmentally friendly to appeal to their customers.
Performance: With increased business and complex technology, there will be a greater load on the system, thus, these systems need to cope with complexity and increased load.
For example, booking airline tickets 20 years ago was far less complex than it is today. The number of travellers and complexity of the system has grown tremendously.
Look and Feel: Every company has to update its website based on new standards and trends in the market. This helps to boost the business and buying experience of the consumer. Some of the e-commerce websites dealing in garments were actually helping consumers get the fitting room experience by allowing them to enter the data and choosing a particular garment. Then, the application would show the buyer how he/she would look in that outfit.
Other: Any other reasons that not listed above.
Let us see what the GAP analysis will look like using these criteria:

This is a high-level document. Readers are strongly recommended to study it in detail for a better result as the GAP analysis (criteria, process, and result) may change based on domain and company's internal policies/culture.
Disclaimer: ISO®, Tropicana®, Hewlett-Packard®, VeriSign® their trademarks and respective product names are used here only for reference to explain the point in the blog.
#Businessanalysis #gapanalysis #anisan #BAtraining #certification #sandhyajane #BusinessAnalysis, #BusinessAnalysisTraining #Businessanalyst #Training #certification #ANISAN #ANISANtechnologies #SandhyaJane #howtolauchbusinessanalystcareer #businessanalysiscourse #career #businessanalysiscareer #BusinessAnalysis #career #BusinessAnalysiscourse #BusinessAnalyst #Chennai #Delhi #Bangalore #Gurgaon #HongKong #Hyderabad #Mumbai #Pune #SandhyaJane #ANISAN #technologies #BusinessAnalysisTraining #certification #Dubai #sydney #London #Tokyo #Shanghai #Beijing #careerpath #businessnalaysiscareer #BA Sandhya Jane, San Francisco, Bangalore, Beijing, Chennai, Delhi, Dubai, Hong Kong, Johannesburg, Kuala Lumpur, London, Mumbai, Hong Kong, New York City, Shanghai, Delhi, Dubai, Sydney, Tokyo, UK, USA, India, China, Australia, Business analysis consulting, consulting services
This is because one of the fundamentals of (personal) financial success is financial discipline which finds practical expression in prudence and accountability. GAP Analysis
ReplyDeleteGap analysis doesn’t have to have any specific template or any standard model however, any artifact which reflects the differences between what is now and what it should really be in an organized way.
ReplyDeleteHuman Resource Consultant in Hosur